Hi there, Welcome to Cli commands by Chronicles. This blog contains a few commonly used CLI commands and is meant for beginners new to CLI.
This guide is a starting point for your journey in CLI.
All of the following commands use the following syntax:
In case of Multiple -modes stated last one will be executed.
General GNU Linux Commands
-
mkdir- It is used to create a directory. The first directory will be treated as root directory.
-
cd- It is used to change the control from one directory to another directory.
To Move out of a directory use the following commands.
$ cd ../-Use to move out of sub directory.
$ cd \-Use to move out of multiple sub directories.- touch-It is used to create a file.
For eg. $ touch Test.txt- It will create an empty text file with name Test.- cat- It is used in 3 ways.
(i). To create a file. The file will be opened in append mode.
$cat >Test.txtTo save press Ctrl+D
(ii). To view content of a file.
$cat Test.txt(iii). To merge the file and Copy the content of one file to another.
$cat A.txt B.txt>Test.txt-
ls-To view number of directories and files in a directory.
$ ls -
ls*- To view files of a specific format.
$ls* .txt - will search the files of format .txt .-
pwd- It is used to view the current working directory.
$pwd -
cp - It is used to copy one file or directory with all its contents from one directory to another.
$cp file.txt ../A- To copy file in same directory.- mv - It is used to move one file or directory from one directory to another.
$ mv file.txt ../A - To move file from one in the same directory.-
head - It is used to print first or more lines in a file.
$ head file.txt -
tail - It is used to print last or more lines in a file.
$ tail file.txt -
tac - It is used to print in reverse order.
$ tac file.txt -
more- It allows us to see large amounts of data at once.
$ more file.txt -
id - It is used to display the id of group and user.
$id -
clear - It is used to clear the screen.
$clear -
vi - Opens Vi text editor to write the programs of text.
$vi -
grep - Filter to search the given pattern in the file content
Syntax: $grep 'string to be searched' File name
For eg.
$grep 'I' C.txt
-
diff - It is used to compare the result of two different files. For eg.
$diff A.txt C.txt -
ping - It is used to check the connectivity status of the server. It returns the number of packets sent, recieverd and round trip times.
$ping google.com -
history - It is used to view all the previous exectured commands in the terminal.
$history -
hostname - It displays the host name.
$hostname -
hostname -i - It displays host ip.
$hostname -i -
chmod - It is used to change the user/group permissions to access file.
Syntax: $chmod u=r/w/x file nameFor eg.
$chmod u=r A.txt- This will change the files permission to read only. -
nl - It is used to display the line numbers of a file.
$nl A.txt -
wc - It gives the Lines, Words and Characters respectively in the available file content.
$wc A.txt -
uniq - It is used to remove duplicate content in a file. It can only remove continuous duplicate content.
$uniq A.txt -
rmdir - It is used to remove specified directory. The directory must be empty.
$rmdir Test -
rm - It is used to remove a file.
$ rm C.txt -
cat /etc/shells - It allows user to view all the files present in /bin directory.
$cat /etc/shellsIt returns the following directories.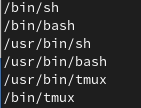
-
which - It allows the user to view the the path to a specific file. For eg.
$which bashreturns the path of the file bash.
-
./ - It is used to execute a file.
Vi Text Editor
The Vi Text editor allows us to view and modify a file using special Vim commands.
The following are basic commands used in a Vim Text Editor.
-
:q- To exit Vim. -
:!- To override previous commands. -
:wq- To write and quit.
Following are the commands that were used to create a bash script and edited using VI editor.
-
To execute a text file as a bash script include
#!/bin/bash. It allows the script to be executed as a bash script. -
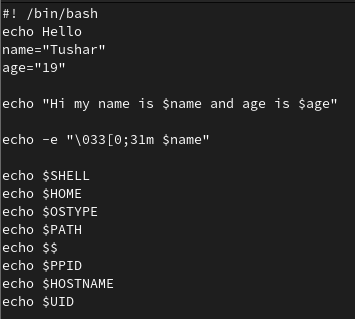
To make a variable in bash script use the following syntax.
$variable name= any valueSometimes we use$declareto create a variable. For eg.$declare Test=100. -
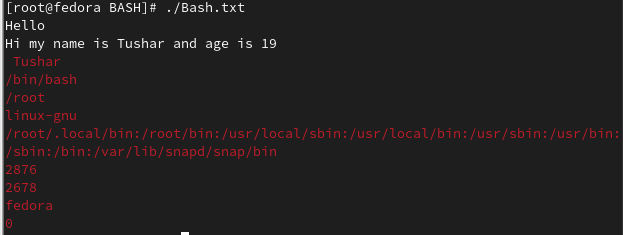
echo - It is used to print on the screen.
$echo Hello. This will print hello on the screen. -
To change the color of the output we use,
echo -e "\033[0;31m TEXT". Depending upon the system used the color will be different in Fedora37, it will print TEXT in RED color.
Enviorment Variables are in Uppercase characters. Following is the list of some variables and their meanings, echo is used to print these variables.
-
$SHELL- It will print the path of Shell. -
$HOME- It will print the path of root directory. -
$OSTYPE- It will print the type of Operating system such as linux-gnu. -
$PATH- It will print the local path. -
$$- It will print the PID(Process ID). -
$PPID- It will print the parent process id. -
$HOSTNAME- It will print the hostname such as fedora. -
$UID- It will print the User ID.
Here is a sample BASH script which was created using Vi editor and prints Enviorment Variables.
Execution using terminal:
-
Change it's permission to make it an executable file.
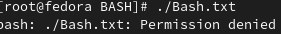

-
Execute using ./ command.